OpenSCAD
Necessary introduction
- CSG modeling
- basic primitives - sphere, cylinder, cube…
- transformation - translation, scaling, roattion…
- set operations - difference, intersection, union
- a tree - all of those are represented as a tree
- OpenSCAD USer Manual – use this
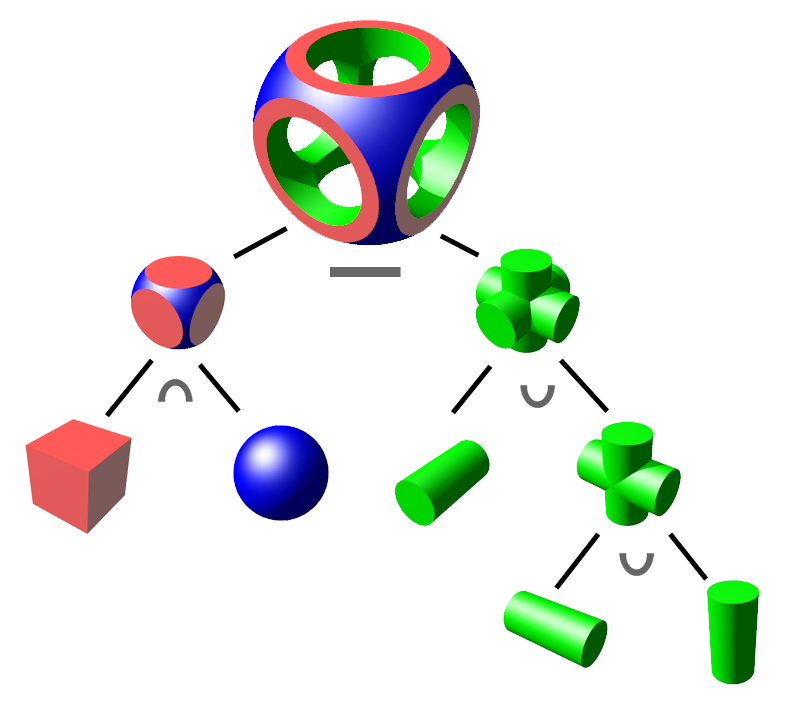
CSG Tree
User interface
- use mouse to manipulate the object
- F5 - fast preview (might not be accurate)
- F6 - full-weight render – export is available after this
- Automatic reload and compile
- more view options (F9, F12, axes…)
Syntax
- C-like – semicolons, curly brackets, comments
- numbers integers or decimals (same type) –
1,0,-5,5.3,9.99998,8/5 - no units, we assume millimeters
- vectors/points in brackets –
[1,2,3]
- numbers integers or decimals (same type) –
- strings in quotes –
echo("Hello world!"); - variables are more like constants
a = 3; echo(a); a= 5;–ECHO: 5
- Mathematical operators and functions, PI
- It’s not programming langue, it’s a descriptive one!
Primitives
cube(size,center);– cuboid (size=[1,2,3]) or cube (size=5)sphere(r);– spherecylinder(h,r1,r2,center);– (frustom of) cpne(r1,r2) or cylinder (r)polyhedron(…);– don’t touch this (it’s MC Hammer)- often use named arguments, as in
cylinder(r=5,h=2); to avoid misinterpretation
Example
cube(150,center=true);
sphere(100);
Transformations
scale()vs.resize()– factor vs. absolute valuerotate([deg,deg,deg])orrotate(deg,[1,1,0])translate([x,y,z])– ralative transformationmirror([1,0,0])– mirroring by planesmultmatrix(…)– transformation matrix (MC Hammer)color()– only for preview, does not work for 3D printing- all is happening around origin (point [0,0,0]) in order
Example
color("green") rotate([0,0,60]) translate([30,0,0]) cube(5);
color("red") translate([30,0,0]) rotate([0,0,60]) cube(5);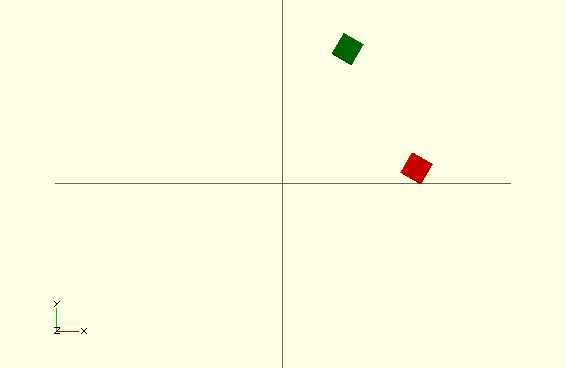
CSG modeling
union()– implicitly performed on the resultsdifference()– remove all other children form the first oneintersection()– intersection of all children- a child is what you pass in
Example
union() {
cube(150,center=true); // first child
sphere(100); // second child
}
Example
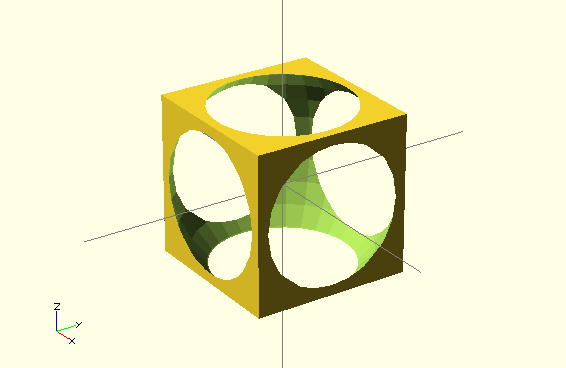
difference() {
cube(150,center=true); // first child
sphere(100); // second child
}
Example
intersection() {
cube(150,center=true); // first child
sphere(100); // second child
}
Loops and conditions
for (z = [-1, 1])– forzin -1 and 1for (i = [0 : 5])– forifrom 0 to 5 (including both)for (i = [0 : 0.2 : 5])– forifrom 0 to 5, with 0.2 stepfor (xpos=[0:3], ypos = [2,4,6])– nested loop with one expression- implicit
union()on results (for efficiency)- therefor there is
intersection_for()– implicitintersection()instead
- therefor there is
- similar syntax for
if (a > b)orif (center == true) - no assignments in for or if bodies
Example
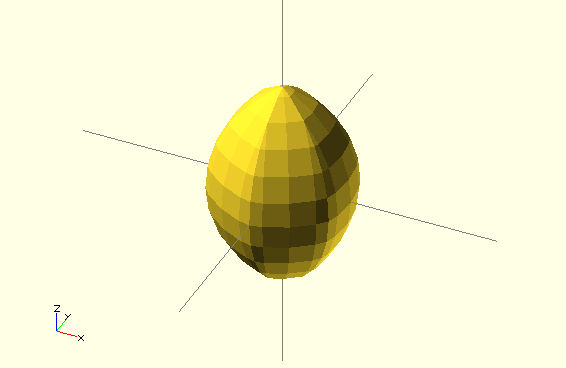
intersection_for(n = [1 : 6]) {
rotate([0,0,n*60]) translate([5,0,0]) sphere(12);
}
Modules
module foo(bar)– like a function or method- “returns” 3D object
- accepts arguments, can have default values
- also can accept children
- can be imported from other files with
include <f.scad>;oruse <f.scad>;useimports modules, *includeimports the whole file
Example
module roundcube(size=1,center=false,corner=1) {
minkowski() {
cube(size,center);
sphere(corner);
}
}
roundcube([50,80,80],corner=5);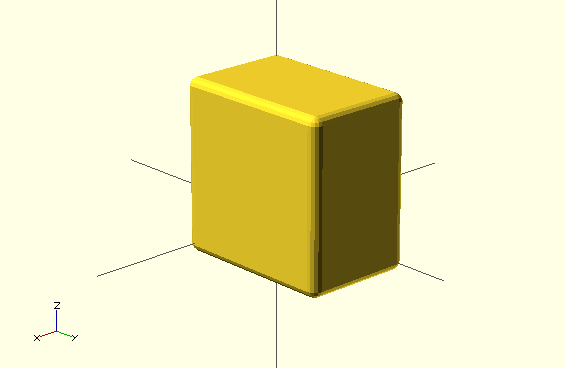
child();
child(0)..child($children-1)children()
Example
module elongate() {
for (i = [0 : $children-1])
scale([10 , 1, 1 ]) child(i);
}
elongate() {sphere(30); cube(45,center=true); cylinder(r=10,h=50);}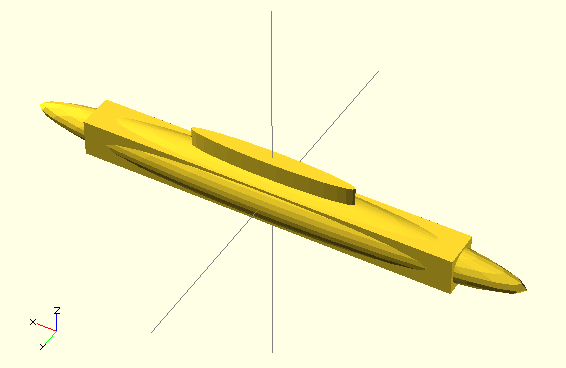
Debugging
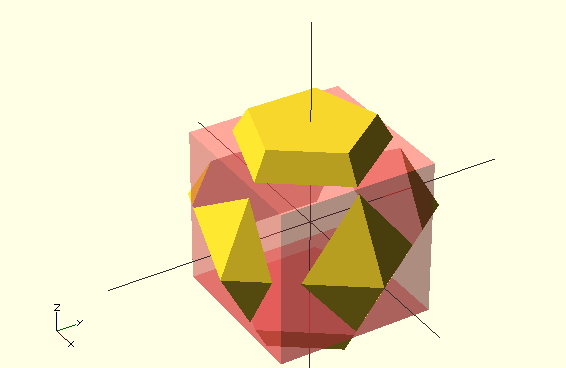
%- in F5 half-transparent, F6 ignored#- in F5 half-transparent, F6 rendered
Example
difference() {
sphere(50,$fn=5);
#cube(65,center=true);
}
Helpers
minkowski()“covers” first child with second, then eventually third…- in fact, it’s minkowski sum (and so it’s commutative and associative)
hull()creates convex hull (puts objects in a minimal “sack”)- both might be quite slow
Example
minkowski() {
hull() {
rotate([120,0,0]) cylinder(h=1,r=10);
translate([0,30,0]) rotate([-120,0,0]) cylinder(h=1,r=13);
translate([0,15,25]) cylinder(h=1,r=8);
}
sphere(3);
}
Two-dimensional subsystem
- there are 2D primitives as well
circle(),square(),polygon()- use
linear_extrude()orrotate_extrude()to make 3D objects
projection()works the other way around (3D to 2D)- more info in the manual
- 2D objects appear as thin 3D objects, but cannot be rendered as such
2D primitives
square()as an alternative tocube()circle()as an alternative tosphere()orcylinder()polygon()as an (easier) alternative topolyhedron()
linear_extrude()
- extrudes 2D shape to third dimension (along Z axis)
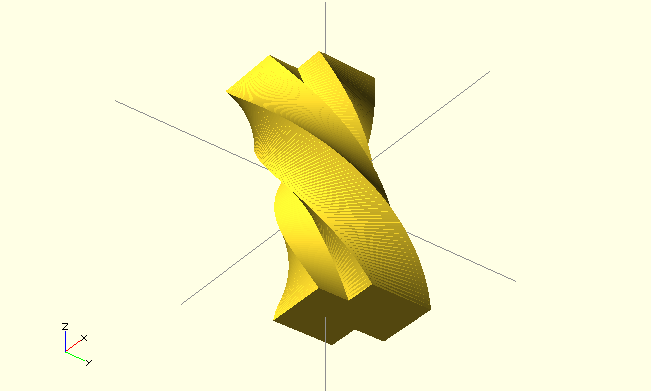
height– height of the extrusioncenter– false extrudes up, true extrudes both direction (each by half height)twist– total rotation of extrude in degreesslices– resolution oftwist– total number of slices
Example
linear_extrude(height=20,twist=180,slices=100,center=true) {
square(5);
square(5,true);
}
rotate_extrude()
- rotates 2D shape to create 3D object
- lifts the object to Z axis
- but rotates it around positive Y
- only draw things to first (positive) XY quadrant
Example
rotate_extrude($fn=200) polygon(points=[[0,0],[2,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4],[0,5]]);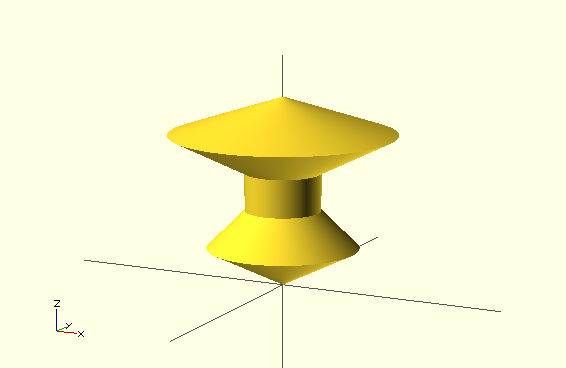
2D import
- you can import DXF as 2D shapes
- How to convert from SVG to DXF
- the conversion might destroy size, use
resize()to be sure
- the conversion might destroy size, use
Example
rotate_extrude() resize([20,0],[true,true]) import("bottle.dxf");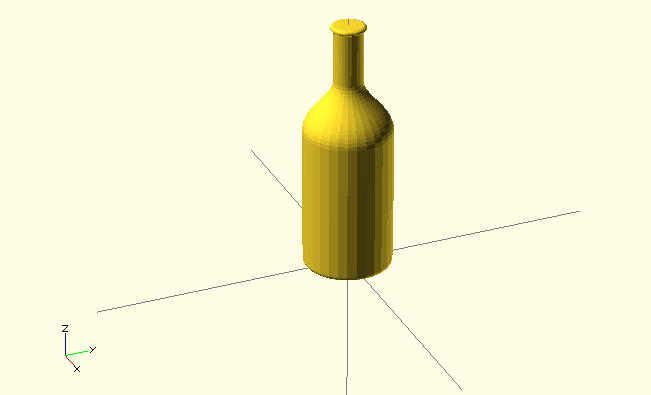
projection()
- projets 3D object to XY plane
cut– true makes obly the slice that intersects XY plane to appear- results in 2D shape
Example
use </usr/share/openscad/examples/example002.scad>
linear_extrude(20) projection() rotate([90,0,0]) example002();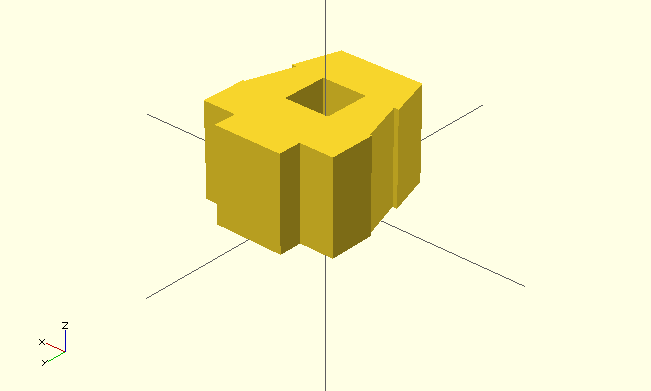
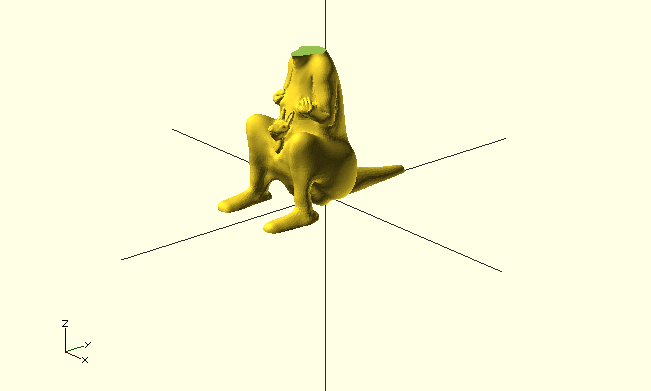
import()
- you can import STL files as well
- not always possible to render
- has to be 2-Manifold
- see 3D models represented in triangular mesh
Example
difference() {
import("kangaroo5.stl");
// http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:33273 CC BY-NC-SA
translate([0,-10,80]) cube(30,true);
}
surface()
surface(file = "smiley.png", center = true);- (Taken from manual)
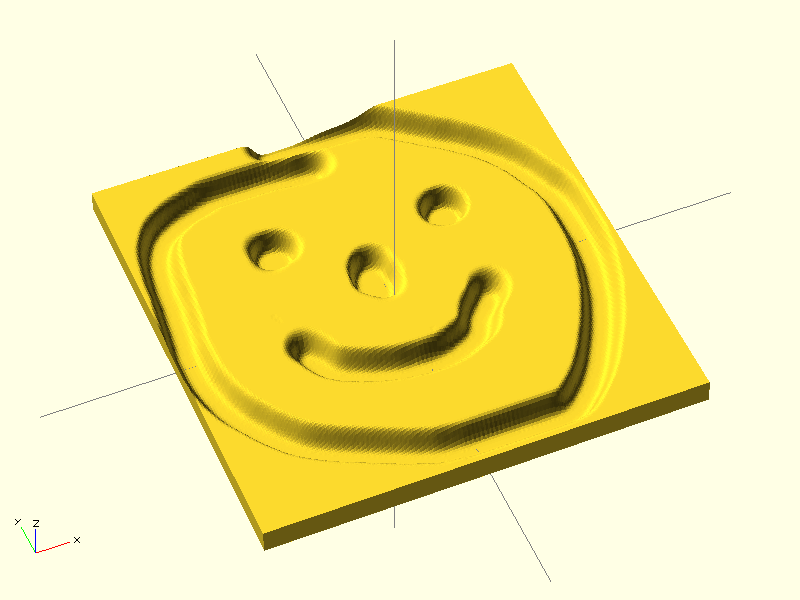

Resolution
$fn,$faa$fsaffects the resolution, see manual for details- can be set globally
- or in a block
- or as an argument to any module or primitive
Simple - 2-Manifold
- for propper STL export it’s necessary to have 2-Manifold objects
- implicit
union()covers most of the issues - possible problem is shared edge (not a real thing in our physical world)
- or badly constructed polyhedron
Example
cube(20); translate([20,20,0]) cube(20);
// e=0.0001; cube(20); translate([20-e,20-e,0]) cube(20);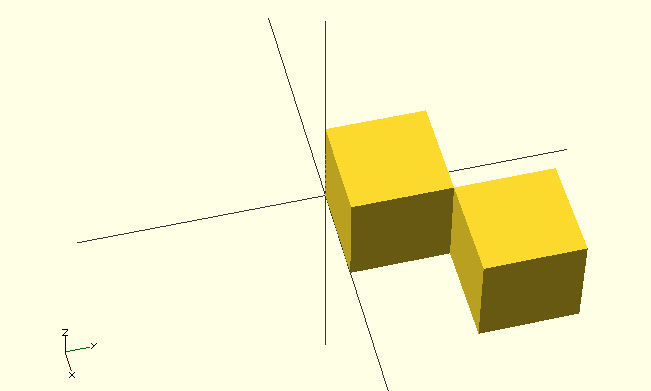
MCAD Library
- lot of basic and complex stuff as well
- more 3D and 2D “almost” primitives such as
pentagon() - has some RepRap stuff
- steppers
- pullys
- has to be
included, notused! - info
- very bad API
Example
include <MCAD/stepper.scad>
motor(Nema17);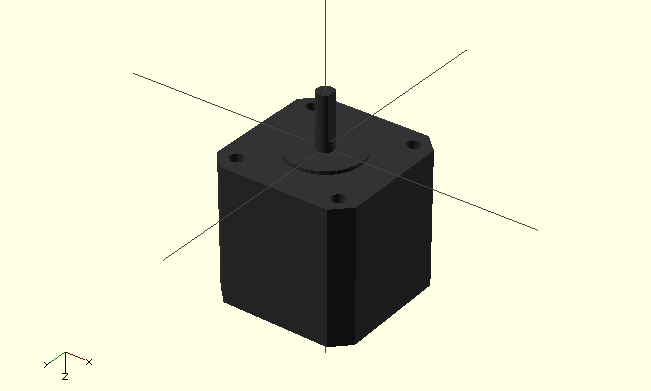
Complex examples
- in OpenSACD
- pastebin