Mesh manipulation in programming
Motivation
Apart from manual mesh manipulation of mesh in apps and tool like netfabb Studio, it is also possible to manipulate mesh with code - creating programs, that manipulate meshes in some more ro less interesting manner. It would be sad not to examine this topic as well being on the Faculty of Information Technology.
ADMesh
ADMesh is open-source CLI tool for STL mesh manipulation and simple repairs. Apart from CLI, there is also C library API.
Short example follows. This loads model.stl (binary or ASCII) and rewrites is as ASCII or binary STL - it converts binary to ASCII and vice versa.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <admesh/stl.h>
int main(void) {
stl_file stl_in;
char *filename = "model.stl";
printf("Opening %s\n", filename);
stl_open(&stl_in, filename);
stl_exit_on_error(&stl_in);
if (stl_in.stats.type == binary) {
printf("Writing ASCII file %s\n", filename);
stl_write_ascii(&stl_in, filename, "ADMesh");
stl_exit_on_error(&stl_in);
} else {
printf("Writing binary file %s\n", filename);
stl_write_binary(&stl_in, filename, "ADMesh");
stl_exit_on_error(&stl_in);
}
stl_close(&stl_in);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}Notice that:
- all functions accepts pointer to instance of
stl_fileas a first argument - there is
stl_exit_on_error()after critical statements (eg. reading and writing to/from filesystem) to avoid segfaults when something went wrong - it is good manner to call
stl_close()when the work is finished
Compile the source with:
gcc source.c -ladmesh
Eventually, if your ADMesh installation is not in your standard PATH:
gcc -L/dir/with/so -I/dir/with/h source.c -ladmesh
We cannot provide instructions for Windows, use standard programming tools for C as if you would like to use any other library.
All structs and function can be found in the header file admesh/stl.h. Unfortunately, there is no documentation.
Task
To get 3 points, program C, C++ or Python tool, that will determine best possible rotation around Z axis for the given file (as first command line argument). Best rotation in this case is such rotation, when the area of smallest rectangle with sides parallel to X and Y axis, that can embrace the 3D model, is smallest.
Look at the bottom side of green cuboid (only corners are drown) - that’s our rectangle.
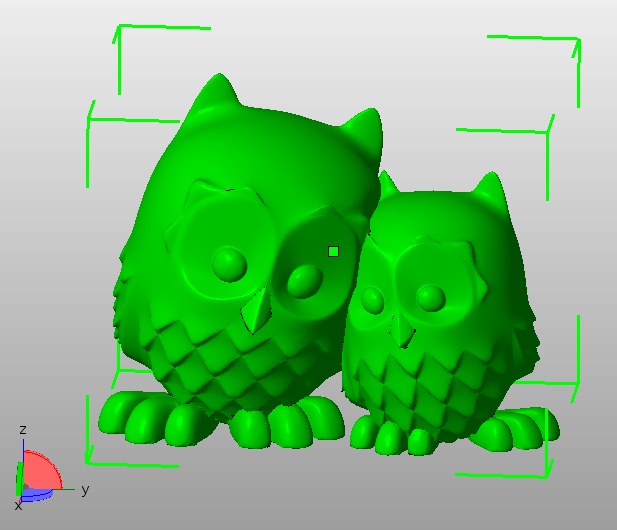
The app will print the best rotation (in degrees) to it’s standard output. It will also save a rotated version of the STL to a second file (second command line argument) - it will be saved in the same format (binary/ASCII) as was the input file loaded. Rotated version will be rotated by the exact same angle as the tool printed.
Best angle can be determined by brute force with angles dividable by 5° (5°, 10°, 15°, …).
Useful functions and data:
stl_rotate_z(&stl_in, angle_in_degrees)- rotates around the Z axisstl_file.stats.number_of_facetsis number of facets/triangles in the meshstl_file.facet_startis a pointer to the first facet (can be used as an array)- facets are saved in
stl_facetstructs that havevertexarray with 3 items, each of them isstl_vertexstruct with 3 floats:x,yandz. - interesting stats (might be useful) are present in
stl_file.stats