3D printing technologies and the RepRap project
Why 3D printing?
- Cheap and fast prototyping (in the matter of hours)
- Easy transformation from graphical designs to physical shapes
- When we are not good enough to sculpture it
- We don’t need/want mass production
- Fun 8-)
Basic principle
How it all works?
All 3D printing technologies share the same principle: putting layers on top of each other - it’s called additive production. It this an opposite of machining. Instead of cutting the object out, you add it up.
3D model is “sliced” into small layers, that are being put on the top of each other. You can imagine it as if you want to create a 3D shape out of paper sheets. You cut the layers of the shape form the paper sheets and than glue them together.
Stereolithography
A method of creating an object from liquid polymer, that is solidified by waves with different amplitude. Video
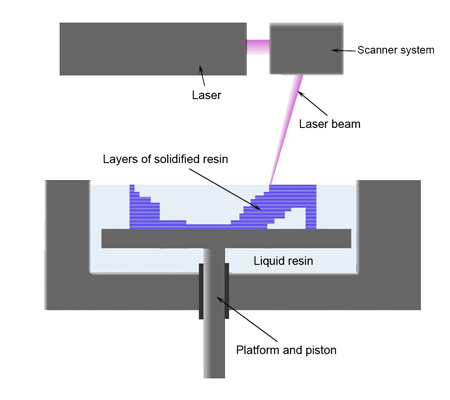
Selective Laser Sintering
A technology based on layering particles and sintering the parts that are supposed to be in the model. Sintering is mostly achieved by laser, eventually by liquid polymer and UV light. SLS, DMLS

PolyJet
Similar to 2D ink printers, polymer is sprayed by little jets. Finally, the layer is solidified by an UV ray. Video
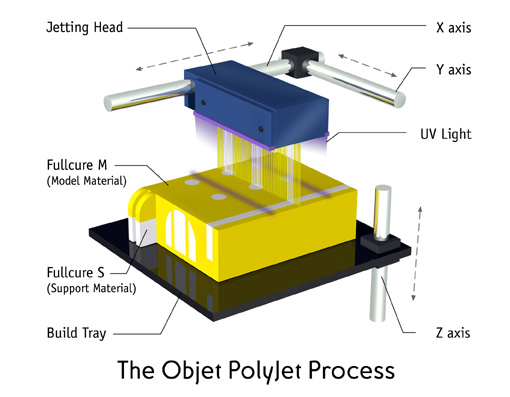
FFF/FDM/Thermoplastic extrusion
FFF (fused filament fabrication) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) a technology based on a principle working like a glue gun. Plastic is pushed to a nozzle, where it is heated, melted and finally deposited on the previous layer or base. Video
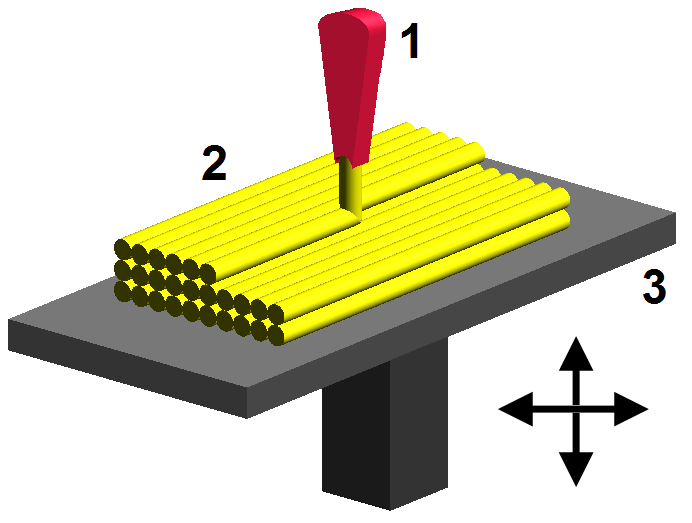
RepRap
- Adrian Bowyer, Uiversity of Bath 2006
- RepRap Darwin, 2007
- RepRap Mendel, 2009
- 3DPrintLab, 2012
RepRap Technology
FFF/FDM
Advantages
- Cheap (printer ~ 400 €, material ~ 20 €/kg)
- OpenSource/OpenHardware
Disadvantages
- Where to get the first printer (chicken/egg)
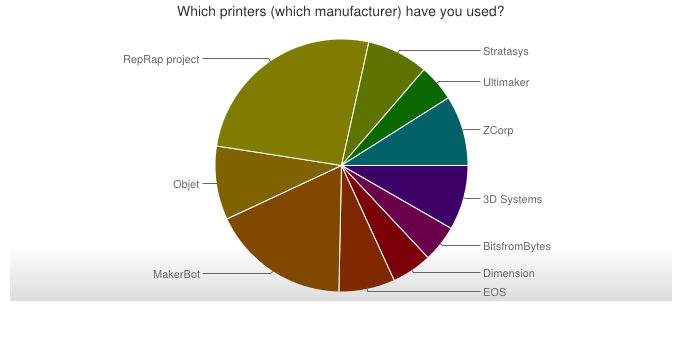
RepRap on the market
Model Darwin
Author: Adrian Bowyer
First RepRap. Print head moves along X, Y axis, the bed is axis Z.
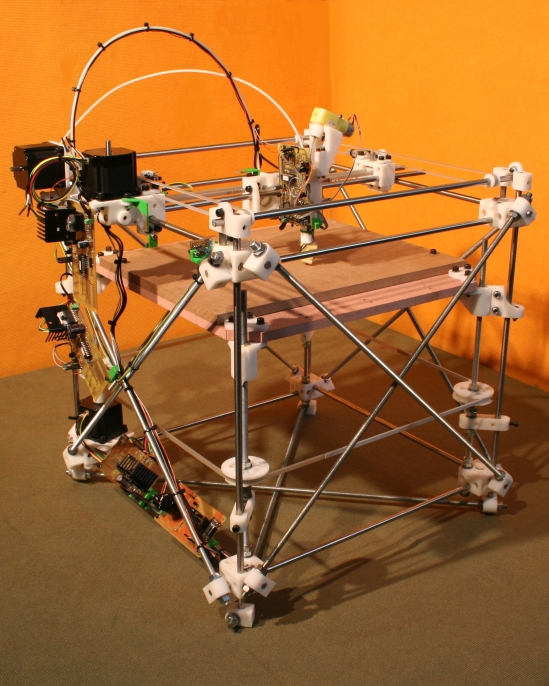
Model Mendel
Author: Adrian Bowyer
Print head moves around X, Z axis, the bed is axis Y.
Model Prusa Mendel
Author: Josef Průša
Updated version of Mendel. Josef Průša reduced the printed parts.
Model Huxley (mini Mendel)
Author: Adrian Bowyer
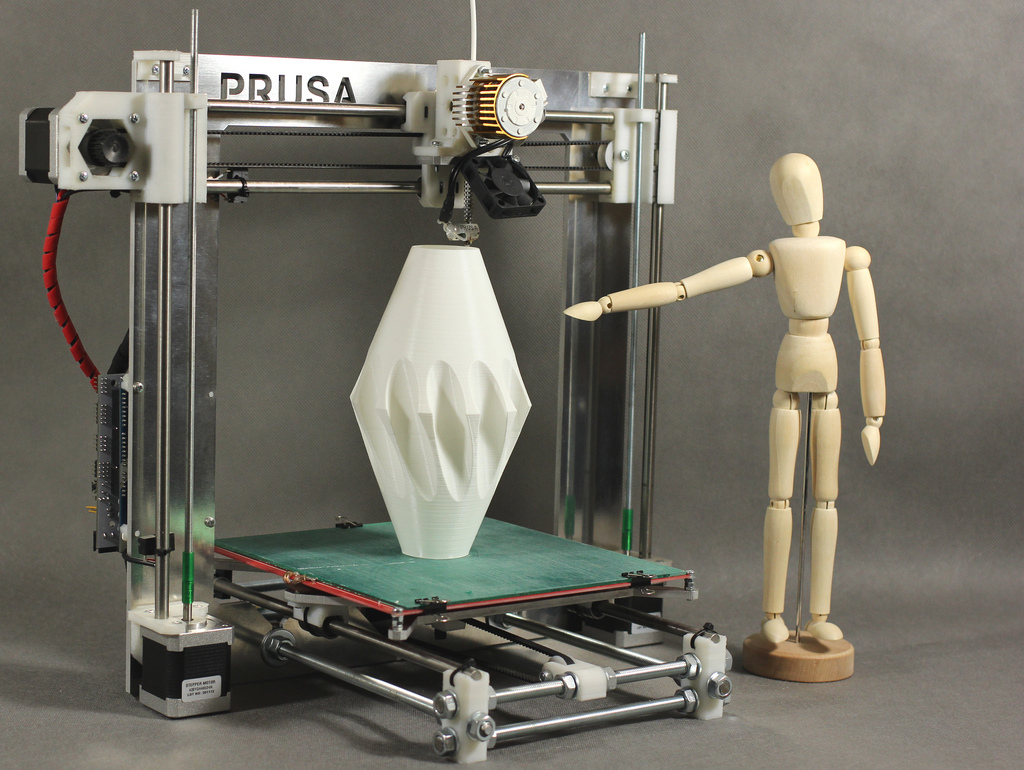
Model Prusa i3
Author: Josef Průša
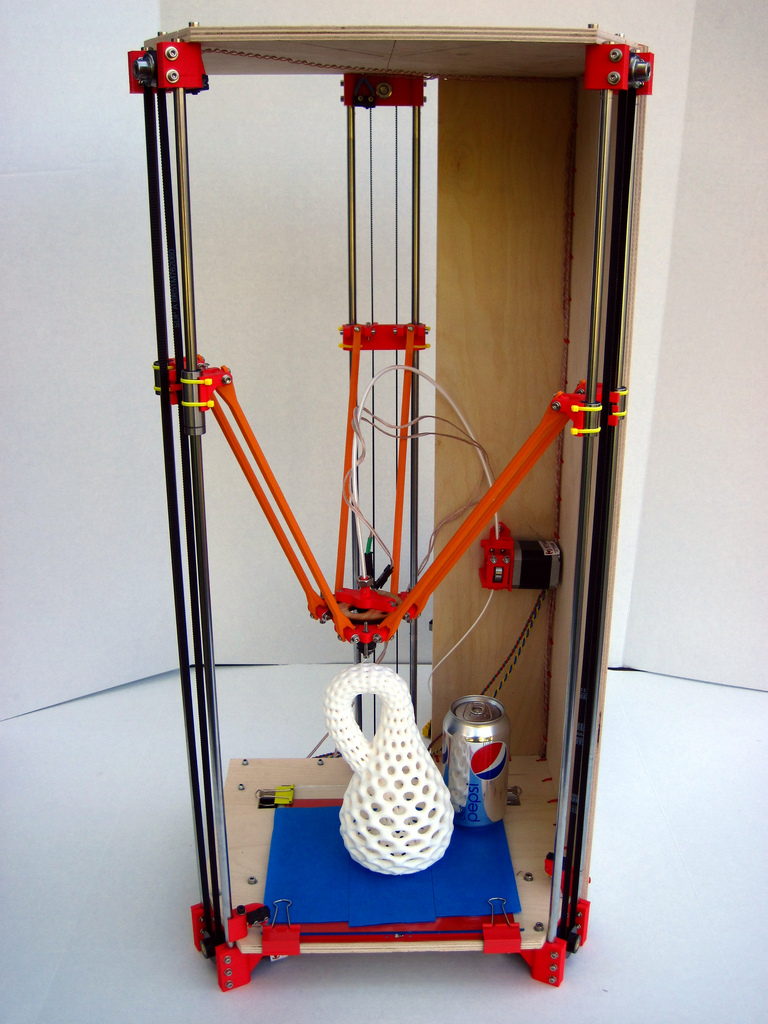
Model Rostock (deltabot)
Author: Johann
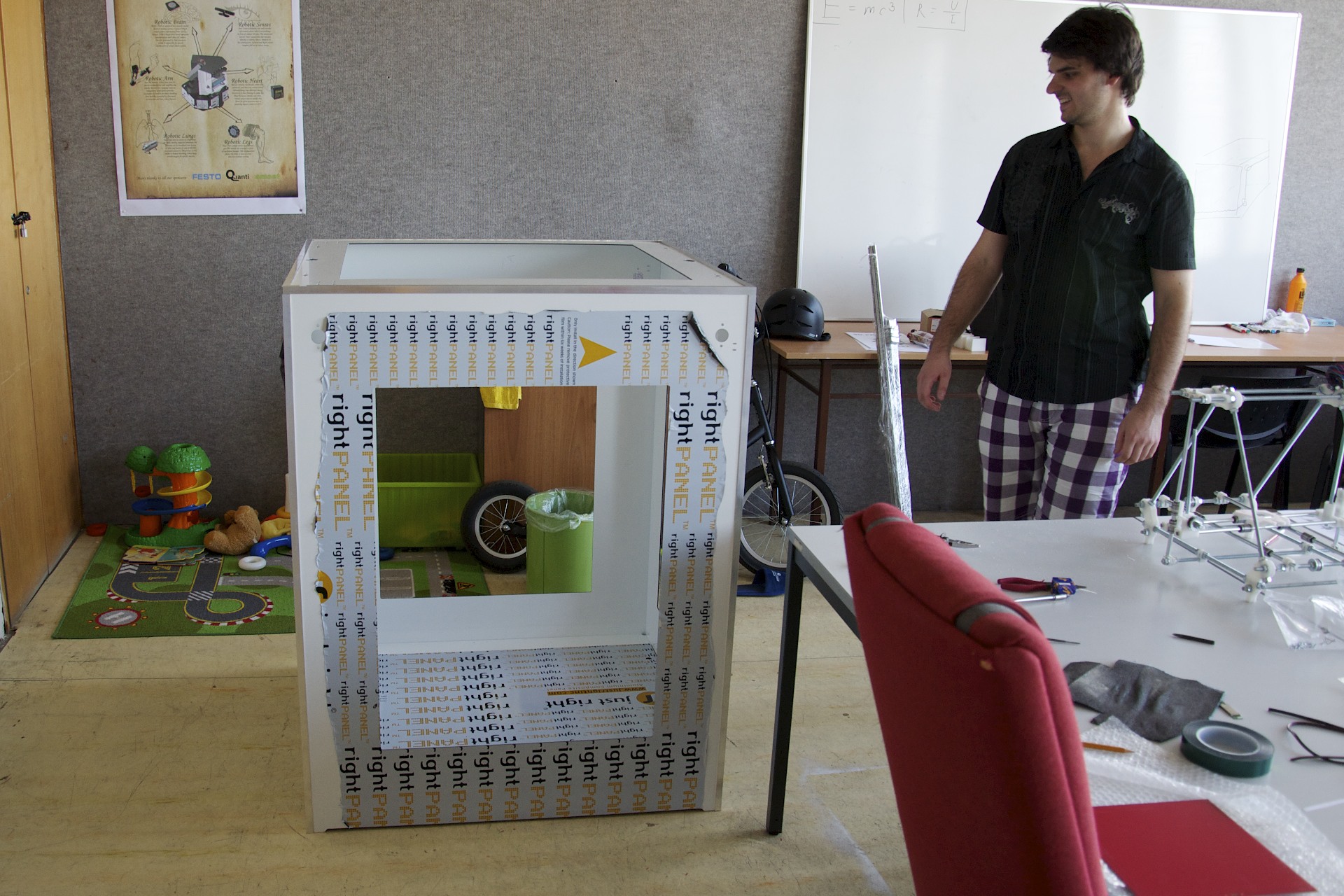
Model Golem
Author: Jan Vaněk


Input format for slicing
STL (STereoLitography) - triangular mesh
Use any software you like.
Input format for the printer
GCode – direct instructions for the hardware
Examples:
- G1 X10 Y10 Z10 E10
- M220 S150
Printing materials
SLA
Photopolymer - to expensive and dangerous for domestic use
SLS
Particles of metal or plastic
FDM/FFF
Plastic filament (wire)
- ABS - LEGO, 3D printers, plastic parts of electronics, cars
- PLA - ecologic, compostable
- Nylon - highly resistant
- PVA - dissolvable in water
- FilaFlex - elastic
- and much
Literature and useful links
Find them in Literature